What is Renewable Energy?
01 Aug, 202310 minRenewable energy is a growing industry, expected to be worth over $2 trillion by 2030. Sourc...

Renewable energy is a growing industry, expected to be worth over $2 trillion by 2030. Sources of renewable energy are helping the world reach net-zero targets and are providing an alternative to the traditional non-renewable energy sources that are causing noticeable damage to our planet. But what is renewable energy, and what are the different types of renewable energy? In this guide, we will delve into these two questions and uncover how renewable energy works and why it is important.
What is renewable energy?
Renewable energy is composed of natural sources that never run out, like the energy captured from the sun via solar panels and wind taken by onshore and offshore wind turbines. Sources of renewable energy also stem from natural elements that can be replenished without further damaging the environment, like organic materials that support the production of bioenergy.
Otherwise known as clean energy, renewable energy is the alternative to non-renewable energy sources such as fossil fuels, coal, gas and oil, which were once the dominant source of energy used globally but have since been revealed to be the catalyst of global warming, posing problems relating to climate change.
How does renewable energy work?
Renewable energy works by converting natural resources into usable energy. These natural sources can come from elements such as wind, the ocean, the sun, and organic waste and can be used for heat, electricity, or transportation. The term 'renewable' refers to the fact that these energy sources are never depleted and can be 'renewed' time and time again.
But what is a renewable energy source? We'll explore this query later in the piece, but first, let's look at why renewable energy is important.
Why is renewable energy important?
Climate change and global warming have been major talking points over the last few decades. With around 80% of the world's energy coming from fossil fuels, governments of the world's nations collectively agree that carbon emissions and greenhouse gases produced by non-renewable energy sources must be cut by at least 50%, with a net-zero target to be met by 2050 to ensure the planet's longevity.
Alternative energy sources and clean energy are playing an important part in ensuring these targets are achieved. They are going some way to resolve the issues caused by decades of relying on fossil fuels to power our lives. The latest findings, as of 2020, of renewable energy accounts for roughly only 30% of global electricity generation.
Despite the above statistic revealing an increase in global renewable energy generation compared to previous years, further evidence of a lack of government investment and commitment could mean we fall short of the 2030 and 2050 targets; the energy produced by renewables is still important to the planet's sustainability.
What are the renewable energy sources?
Solar Energy
Solar energy involves harnessing radiant light and heat from the sun to be used in renewable energy tech like solar power to produce electricity and solar thermal energy to create heat.
Regarding solar power, photovoltaic (PV) systems and solar panels can be installed to convert solar cells produced by sunlight into electricity. These panels and systems can stretch across numerous acres within solar farms to provide electricity to be stored in power grids to power entire cities or can be applied to the roofs of residential buildings to power people's homes.
On the other hand, solar thermal energy is created through concentrated solar-thermal power (CSP) systems that use mirrors and lenses to capture radiant energy from the sun to generate heat and electricity. CSP systems are often used in large power plants to power turbines and engines.
Key solar energy facts
- Solar energy is captured by the sun and therefore provides an endless supply of energy
- The global market size of solar energy is growing at a CAGR of over 7% and should exceed $300 billion by 2030
- China produces the most solar energy with 392 GW
- The cost of installation dropping more than 80% over the last decade, helping the global population cut the cost of energy bills
- As of 2023, the average price for a 350W solar panel is £726
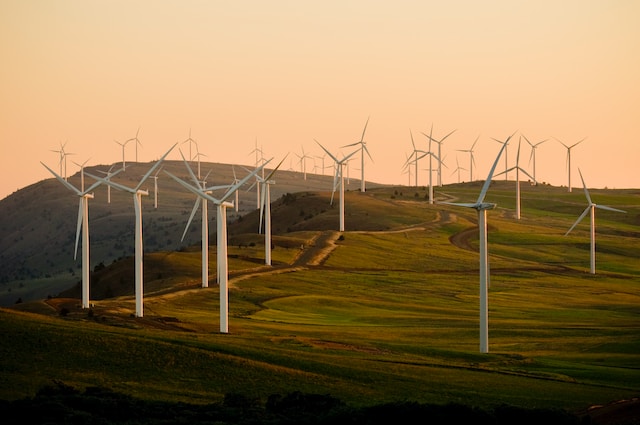
Wind Energy
Wind energy or wind power is a renewable energy source that involves the use of wind turbines to catch the kinetic energy produced by wind and convert it into electricity.
When a wind turbine's blades spin due to the force of the wind, the rotor to which they're attached spins a generator that captures the kinetic energy and turns it into electricity. This mechanical energy is then transmitted to a substation and distributed to homes and businesses.
A wind turbine is built up of various components but is typically made up of three main parts:
The rotor
The rotor is made up of three blades that are attached to a central hub. The blades are angled so that when they spin, they catch the wind
The nacelle
The nacelle is the housing that contains the generator, which converts the kinetic energy into electricity
The tower
The tower supports the nacelle and rotor
There are two types of ways wind energy is produced:
Onshore wind energy
Onshore wind farms are based on land in locations like open fields, hills, and coastlines where wind speeds are high.
Offshore wind energy
Offshore wind farms are located in the ocean, where wind speeds are often greater than on land.
Key wind energy facts
- Wind power is a clean source of renewable energy
- The world's largest offshore win farm, Hornsea 2, is located in Yorkshire, England and is made up of 165 wind turbines that have the potential to power 1.4 million UK households.
- Total win installation capacity reached 906 GW in 2022, a 9% increase compared with the previous year
- The worlds largest onshore wind farm, the Gansu Wind Farm, China, has the potential to generate enough energy to power a small country
- By 2030 the global market of wind energy is expected to hit over $150 billion
Bioenergy
Bioenergy is energy derived from organic matter or biomass and is a versatile renewable energy source. Biomass can be anything from plants and trees to agricultural, food waste, and even sewage. The energy from biomass can be converted into liquid fuels as an alternative to the fossil fuels that power transport. Additionally, bioenergy can be anything from electricity, heat, and biofuels and has a lower carbon footprint than traditional fossil fuels.
There are many different ways to produce bioenergy. For example, dry, combustible feedstocks such as wood pellets can be burnt in furnaces to generate heat, which can be used to generate electricity or heat homes and businesses.
Another example of how biomass creates bioenergy is through wet feedstocks, such as food waste. This waste can be put into sealed tanks where they rot and produce methane gas, also known as biogas. The gas can be captured and burnt to generate electricity or injected into the national gas grid and used for cooking and heating.
Key bioenergy facts
- The use of bioenergy has grown at an average rate of 7% per year over the past decade
- Bioenergy waste-to-energy projects are reducing the amount of waste produced at landfill sites (a hub for methane production) by nearly 90%
- By 2030 the global market size of bioenergy is expected to be over $200 billion
- By 2050, solid bioenergy is expected to account for 60% of global bioenergy demand, liquid biofuels for 30% and biogases for 10%
- Bioenergy accounts for 55% of all renewable energy and more than 6% of the global energy supply
Hydroelectric Energy
Hydroelectric energy, otherwise called hydropower, is a renewable energy source known for generating electricity from the movement of water. This source of renewable energy is created at hydroelectric power plants. These plants use the force of falling water stored behind a dam or reservoir to turn turbines, which makes kinetic energy that can be converted to electricity.
Here's an overview of how hydroelectric energy works:
- Water is collected in a reservoir behind a dam or diverted from a river or stream
- The water flows through a pipe called a penstock that controls the water flow to a turbine
- Once the water gets to the turbine, the blades of the turbine are turned by the force of the water
- The turbine is connected to a generator, and as the blades turn in the water, this converts the kinetic energy of the turbine into electrical energy
- Electricity is then transmitted to homes, businesses, and industries through power lines
Key hydroelectric energy facts
- Hydropower is one of the largest sources of renewable energy, generating nearly 60% of all renewable energy
- 16% of all sources of generated energy comes from hydroelectric energy
- In 2022, the total installed capacity of hydroelectric power plants worldwide reached 1.39 million MW - an 8-year high
- Hydroelectric energy is one of the oldest sources of renewable energy, dating back thousands of years to the Greeks, who used the flow of water to power the wheels of their mills to ground wheat into flour
- By 2030, the global market size of hydropower is expected to exceed £370 billion
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source that takes the heat and thermal energy stored in the water and rocks from the Earth's core and converts it into electricity and heat for use in homes and industrial buildings.
The heat extracted from the rocks and fluid originates from the planet's birth over 4 billion years ago and comes from around 1,800 miles below the Earth's crust. Much of this heat is sourced from the Earth's molten rock, known as magma, and potassium-40 and thorium-232, decaying radioactive isotopes.
Geothermal energy has three main types:
Dry steam
Dry steam geothermal power plants use vapour produced naturally underground. The steam is piped from underground wells to a power plant, which is directed into a turbine and generator unit.
Flash steam
Flash steam geothermal power plants use hot water produced naturally underground. Hot water is pumped into a chamber where it is flashed into steam. From here, steam is piped into a turbine generator unit, where it is used to generate electricity.
Binary cycle
Binary cycle geothermal power plants use hot water generated naturally underground. This hot water is used to heat a fluid with a lower boiling point than water. The heated liquid vaporises and turns a turbine generator unit, which produces electricity.
Key geothermal energy facts
- Global geothermal energy capacity reached 14.9 GW in 2022
- 27 countries contributed to the generation of around 92 billion kWh of geothermal energy in 2021
- The US generates the most geothermal energy in the world, producing over 3.7 GW. They're also home to the largest geothermal plant in the world, The Geysers, located in San Francisco, California
- Geothermal energy can generate electricity 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
- In 2023 the geothermal market size is expected to reach over $7 billion and is expected to climb over $9 billion by the end of the decade
Final Thoughts
Renewable energy is a sustainable and clean source of energy, helping us reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and combat climate change. As discussed, there are many different types of renewable energy, and each has the potential to play a significant role in our energy future.
As the world's population continues to grow and our demand for energy increases, it is more important than ever to turn to these sustainable renewable energy sources to meet our energy needs. Renewable energy is a vital part of the solution to our energy crisis and has the potential to create millions of new jobs to power renewable projects for global organisations.
Looking to grow in the renewable energy industry?
For over two decades, we have been a leading renewable energy solutions provider, partnering with our global clients to deliver workforce solutions, from talent sourcing to project management.
Our dedicated renewable energy team has extensive knowledge of the industry and its challenges. We have a global network of talent and local market expertise that allows us to find the right people for your project, no matter where in the world.
We are currently working on some of the world's most exciting projects in the world of renewables and have access to a wide range of renewable energy job opportunities for engineers and other professionals looking to advance their careers in the renewable energy industry.
If you are looking for a partner who can help you achieve your renewable energy goals, contact NES Fircroft today to discuss your needs and how we can help you succeed.